
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

27-05-2025 - Physics - Reflection and refraction [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_11)
Reflection and refraction

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
When we talk about reflection and refraction we must immediately enter a new world, that of optical physics. Reflection and refraction are two fundamental phenomena of optical physics that describe the behavior of light or other types of waves when they encounter a surface of a medium.
Synthetically we can state the following:
Reflection = phenomenon by which a wave bounces off a surface. In this case it does not pass through it.
Refraction is the phenomenon by which a wave changes direction and speed when it passes from one medium to another. The most classic example of refraction is observing a straw in a glass of water. At the point where the straw enters the water the straw appears broken.
The formulas of reflection and refraction
The law of reflection is simple and is as follows:

WHERE:
θi = angle of incidence
θr = angle of reflection
The law of refraction is the following:

Where:
n1 and n2 = refractive indices of the two media
θ1 = angle of incidence
θ2 = angle of refraction
n = refractive index
In turn, the refractive index is the speed of light in a vacuum divided by the speed of light in the medium it is passing through.
That is:

Where:
c = speed of light in a vacuum
v = speed of light in the medium considered
Geometric optics
Geometric optics represents an approximate method that allows us to study the behavior of light in free space, that is, when it encounters
discontinuities of dimensions much larger than the wavelength.
In simpler words, we could say that we use geometric optics to describe the propagation of light as straight lines, without considering wave effects. So it is a method that excludes a part of the real study, that is, how it should be done in reality, but it is still a useful and accurate method in a large part of the cases.
Light wave in a medium
Let's clarify a concept right away, in the previous articles we had already expressed the following, a light wave is a form of electromagnetic wave that transports energy in the form of light
When we talk about waves we must talk about three characteristics that they can have:
-Wavelength, which is the distance between two successive crests. Usually expressed with the letter λ.
-Frequency, which is the number of oscillations per second
-Speed. In a vacuum the speed is 300,000,000 m/s, which is equivalent to 300,000 km/s
Reasoning
A light wave passes from a vacuum, and which has a refractive index of reference therefore unitary, with a certain wavelength λ0, in the medium which has a refractive index n, it will propagate with a wavelength given by the following mathematical expression:

IMPORTANT
From what we have written up to now it is easy to deduce what is written below, but if this were not the case, we must still consider that the following statement is very important.
The wavelength in a medium is always less than that possessed by the wave in a vacuum.
Scholars who worked on Reflection and refraction
Willebrord Snell
Willebrord Snell (1580-1626) was a Dutch mathematician and astronomer and is the one who discovered the law of refraction (the one shown above and which I report below without the specifications)
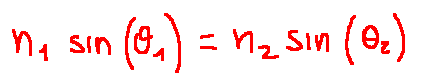
Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens (1629-1695) was a mathematician, physicist and Dutch astronomer and formulated what we now call Huygens' Principle.
Huygens' principle is also called the wave principle of light and states that every point of a wave is the origin of secondary waves.
This principle is the basis of modern physical optics.
Conclusions
Reflection and refraction are two physical phenomena. Reflection is light bouncing off a surface, refraction is light changing direction when entering a medium. Reflection is used to design optical fibers, refraction is used to design lenses and glasses.
Question
Did you know that the Dutch physicist Huygens, who formulated the wave principle, also invented the first accurate pendulum clock, which revolutionized time measurement.

ITALIAN

27-05-2025 - Fisica - Riflessione e rifrazione [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_11)
Riflessione e rifrazione

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Quando parliamo di riflessione e di rifrazione dobbiamo subito entrare in un mondo nuovo, quello della fisica ottica. La riflessione e la rifrazione sono due fenomeni fondamentali della fisica ottica che descrivono il comportamento della luce o di altri tipi di onde quando incontrano una superficie di un mezzo.
Sinteticamente possiamo affermare quanto segue:
La riflessione = fenomeno per cui un'onda rimbalza su una superficie. In questo caso non la attraversa.
La rifrazione è il fenomeno per cui un'onda cambia direzione e velocità quando passa da un mezzo ad un altro. L'esempio più classico della rifrazione è osservare una cannuccia in un bicchiere d'acqua. Nel punto in cui la cannuccia entra nell'acqua la cannuccia sembra spezzata.
Le formule della riflessione e della rifrazione
La legge della riflessione è semplice ed è la seguente:

DOVE:
θi = angolo di incidenza
θr = angolo di riflessione
La legge della rifrazione è la seguente:

Dove:
n1 e n2 = indici di rifrazione dei due mezzi
θ1 = angolo di incidenza
θ2 = angolo di rifrazione
n = indice di rifrazione
A sua volta l'indice di rifrazione è la velocità della luce nel vuoto diviso la velocità della luce nel mezzo che si sta attraversando.
Ovvero:

Dove:
c = velocità della luce nel vuoto
v = velocità della luce nel mezzo considerato
Ottica geometrica
L’ottica geometrica rappresenta un metodo approssimato che permette di studiare il comportamento della luce nello spazio libero ovvero nel caso in essa incontri
discontinuità di dimensioni molto maggiori della lunghezza d’onda.
In parole più semplici potremmo dire che ci serviamo dell’ottica geometrica per descrivere la propagazione della luce come linee rette, senza considerare gli effetti ondulatori. Quindi si tratta di un metodo che esclude una parte dello studio reale, cioè di come dovrebbe essere fatto nella realtà, ma risulta comunque un metodo utile e accurato in una gran parte dei casi.
Onda luminosa in un mezzo
Chiariamo subito un concetto, negli articoli precedenti avevamo già espresso quanto segue, un'onda luminosa è una forma di onda elettromagnetica che trasporta energia sotto forma di luce
Quando si parla di onda dobbiamo parlare di tre caratteristiche che esse possono avere:
-Lunghezza d'onda, che è la distanza tra due creste successive. Solitamente espressa con la lettera λ.
-Frequenza, che sono il numero di oscillazioni al secondo
-Velocità. Nel vuoto la velocità è di 300.000.000 m/s, che equivalgono a 300.000 km/s
Ragionamento
Un’onda luminosa passa dal vuoto, e che ha indice di rifrazione di riferimento quindi unitario, con una certa lunghezza d’onda λ0, nel mezzo che ha indice di
rifrazione n, essa propagherà con lunghezza d’onda data dalla seguente espressione matematica:

IMPORTANTE
Da quello che abbiamo scritto fino ad ora è facilmente deducibile ciò che è scritto qui di seguito, ma se così non fosse, dobbiamo comunque considerare che la seguente affermazione è molto importante.
La lunghezza d’onda in un mezzo è sempre minore di quella posseduta dall’onda nel vuoto.
Studiosi che hanno lavorato sulla Riflessione e rifrazione
Willebrord Snell
Willebrord Snell (1580-1626) è stato un matematico e astronomo olandese ed è colui che ha scoperto della legge della rifrazione (quella mostrata in precedenza e che riporto qui sotto senza le specifiche)
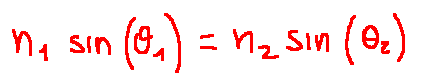
Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens (1629-1695) era un matematico, fisico e astronomo olandese e formulò quello che oggi chiamiamo Principio di Huygens.
Il principio di Huygens è anche chiamato principio ondulatorio della luce e afferma che ogni punto di un’onda è origine di onde secondarie.
Questo principio è la base della moderna ottica fisica.
Conclusioni
La riflessione e la rifrazione sono due fenomeni fisici. La riflessione è la luce che rimbalza su una superficie, la rifrazione è la luce che cambia direzione entrando in un mezzo. Il fenomeno della riflessione è usato per progettare fibre ottiche, il fenomeno della rifrazione è usato per progettare lenti e occhiali.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che il fisico olandese Huygens, che formulò il principio ondulatorio, inventò anche il primo orologio a pendolo preciso, che rivoluzionò la misurazione del tempo.
THE END
This is perfectly explained in simplicity. I remember always enjoying this particular topic every single time I heard it
Thanks for stopping by and I’m glad to hear that you liked this topic. Regarding refraction, studies start with Ptolemy, but it seems that around the year 1000 a certain Alhazen (Ibn al-Haytham) even wrote a book called “The Book of Optics”, which could be considered the first serious approach to the refraction of light. Refraction is a topic that has attracted scholars since ancient times. !HUG
To understand this better, will someone need a logarithm table or book?
Hello and thank you for leaving a comment. To better understand refraction and reflection of light there is a simple book to read which is “The light” by Alberto Rojo and Anthony M. Sadar. A book with a more scientific approach could be “Fundamentals of Optics” by Francis Jenkins and Harvey White. I personally have never read them. These two books were on the list of books recommended by my physics professor !PIZZA
Your way of presenting made it easy to understand important concepts in light physics, especially distinguishing the laws and giving simple explanations with examples like "the straw in water."
Thank you for your kind comment. I try to explain things in a technical and simple way. In my opinion, technical topics, if not explained in a simple way, can be incomprehensible. I would prefer that more and more people understand how physics is at our side in everyday life !hiqvote
Ecco, riflessione e rifrazione non li ho mai studiati ne a scuola ne all'università pur facendo fisica... Certo che non avrei mai detto fossero arricati così avanti nel suo studio già nel 1500-1600
!PIZZA
Non so se sia una leggenda, ma giá Tolomeo nel II secolo d.C. studió la rifrazione in modo quantitativo… sembra che sia stato trovato un libro chiamato Optica, un trattato sulla rifrazione. Peró gli anni che hanno segnato una svolta scientifica sono stati quelli che hai citato nel commento !HBIT
#hive #posh
@stefano.massari, you're rewarding 3 replies from this discussion thread.
$PIZZA slices delivered:
davideownzall tipped stefano.massari
@stefano.massari(1/5) tipped @bisolamih
Come get MOONed!